TI-RSLK Path Follower
ECE 3 Final Project
The goal of this project was to develop a path-following car based on the TI-RSLK car platform using a series of IR sensors and a PID controller. Code for the path-following system can be found here, and code for the basic Arduino PID controller that was used can be found here.
The path-following system began with an auto-calibration routine in which the car was placed over a white area, followed by a black area, from which minimum and maximum values were calibrated for each sensor. To calculate error values from the aggregated sensor data, initial readings were taken at various distances from the path, as shown below:
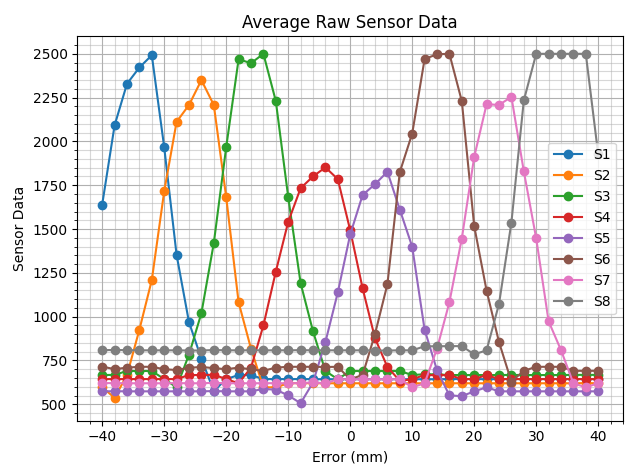
This data was then normalized:
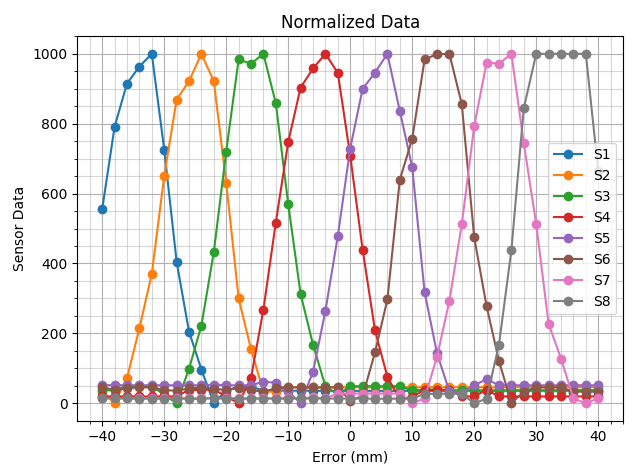
The normalized data was then combined via three different weighting schemes to produce a single error value corresponding to the distance between the center of the car and the center of the track:
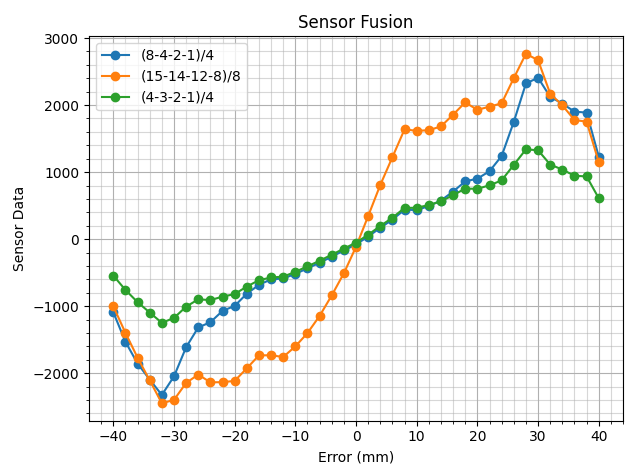
For the actual path-following system, the weighting scheme shown above in green was selected, and only a PD controller was used. During each iteration of the PD loop, its output was added or subtracted from a base wheel speed for the left and right wheels of the car to cause the car to turn towards the path (although percentage-based speed compensation would have perhaps worked better and produced more consistent performance across high and low speeds).